leatherback turtle
| Family | Dermochelyidae |
|---|---|
| Genus | Dermochelys |
| IUCN category (World) | VU |


Introduction
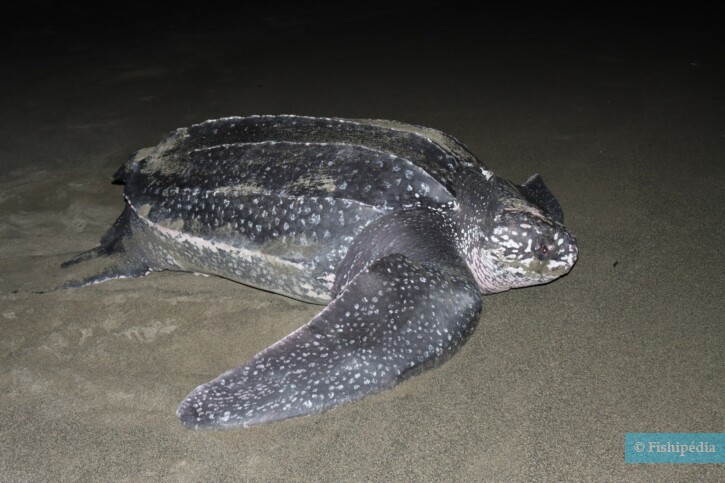
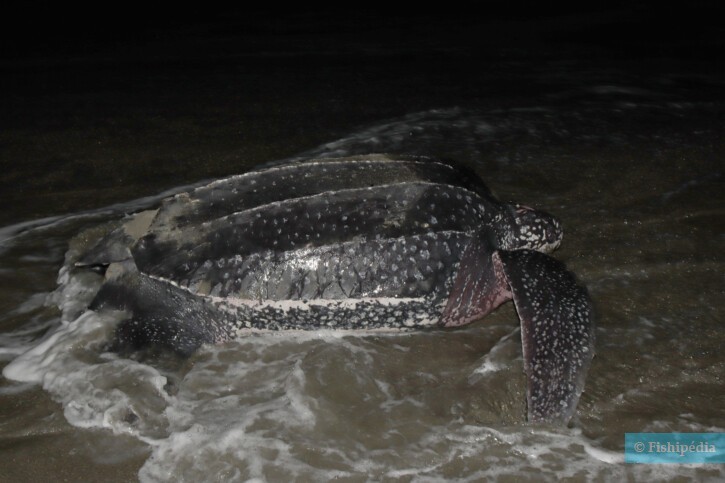
Dermochelys coriacea, commonly known as leatherback turtle, is a salt water reptile.
This sheet is currently being prepared. The texts currently proposed come from our data model or are being drafted. To request priority for this content, you can write to us HERE.
Who is it?
Morphology
-
Type
-
Size160 - 200 cm
-
Weight400 - 900 kg
-
Longevity90 year
-
Type
-
Size160 - 200 cm
-
Weight400 - 900 kg
-
Longevity90 year
How to recognize This reptile ?
The leatherback turtle measures between 160 and 200 cm. This reptile is unicolore with a predominantly noir and gris body.
Behaviour & Life cycle
-
Sociabilitysolitary
-
Way of livingdiurnal
-
VenomousNo
-
Dietpredator
This species is known to emit sounds easily audible by humans.
The leatherback turtle is a reptile solitary. This species is carnivorous .
Although the leatherback turtle is non-territorial, it is sometimes aggressive towards other species. In a constant quest for dominance, the dominant males of this species cannot stand each other. The battle between two individuals can be intense and violent. It will result in the submission and sometimes even death of one of the protagonists.
Reproduction
-
Reproductionovipare qui enfouit ses œufs
-
Migratory speciesYes
-
Clutch size60 - 140 eggs
The leatherback turtle is a reptile ovipare qui enfouit ses œufs.
Risks for humans
-
VenomousNo
-
BiteYes
This species can attack if it feels threatened. It is important to be particularly vigilant especially during dives or fishing sessions.
Origin and distribution
Conservation status of populations (IUCN)
What is its habitat?
Natural environment characteristics
-
Temperature5 - 25 °C
-
Depth0 - 1000 m
-
EnvironmentActive pelagic
Biotope presentation
The leatherback turtle is most often found at a depth between 0m and 1000m. However, it is not impossible to find this species at other depths.
Species of the same biotope
To go further
Sources & Contributions
Participation & Validation
The Fishipedia team and specialist contributors are committed to providing high-quality content. However, although the information comes from scientific sources or testimonials from specialists, the cards may contain inaccuracies.

Théo Guillaume
Translation
Translation done with the valuable contribution of our translators, who make this information available to a wider audience. We sincerely thank them for their commitment.
Bibliographic references
- - GBIF
- - Effects of illegal harvest of eggs on the population decline of leatherback turtles in Las Baulas Marine National Park, Costa Rica - Tomillo, P. S. - Saba, V. S. - Piedra, R. - Paladino, F. V. - Spotila, J. R. - Conservation biology - 2008.
- - Maternal investment in reproduction and its consequences in leatherback turtles - Wallace B. P. - Sotherland, P. R. - Santidrian Tomillo P. - Reina R. D. - Spotila, J. R. - Paladino F. V. - Oecologia - 2007.
- - Nesting ecology of the leatherback turtle, Dermochelys coriacea, at Parque Nacional Marino las Baulas, Costa Rica - Reina R. D. - Spotila, J. R. - Piedra, R. - Paladino F. V. - Mayor, P. A. - Copeia - 2002.
- - Presence de la tortue luth Dermochelys coriacea dans les eaux tunisiennes - Bradai, M. N. - El Abed, A. - Rapp. Comm. int. Mer Medit - 1998.
Scientific partners
Tags
#Dermochelyidae
#Dermochelys
#plein eau
#Turtle
#Bay of Bengal
#Gulf of Mexico
#Persian Gulf
#Great Barrier Reef
#mer d'Oman
#East China Sea
#Tasman Sea
#Caribbean Sea
#Philippine Sea
#Sea of Japan
#Mediterranean Sea
#Red Sea
#South East Asian Seas
#Indonesian seas
#Océan Atlantique Bahamas
#Océan Atlantique Bermudes
#Atlantic Ocean: North Coast of Brazil
#Océan Atlantique Est Afrique - Angulhas
#Océan Atlantique Est Afrique - Bengala
#Océan Atlantique Est Afrique - Golfe de guinée
#Temperate Eastern Atlantic Ocean
#Océan Atlantique Est Afrique - Transition & Cap Vert
#Eastern Cold Atlantic Ocean
#Gough Island
#Saint Helena
#Cold temperate Northwest Atlantic Ocean
#Northwest warm temperate Atlantic Ocean
#Southwest warm temperate Atlantic Ocean
#Eastern tropical Atlantic Ocean
#Southwest Tropical Atlantic Ocean
#western Indian Ocean
#Desventuradas Islands
#Galapagos
#Océan Pacifique Nord Est Tempere Chaud
#Océan Pacifique sud-est tempéré chaud
#Tropical Eastern Pacific
#Western Tropical Pacific Ocean
Species of the same biotope





















